Binderized HAL (HIDL)
In a Binderized HAL, the Android framework and HALs communicate with each other using binder inter-process communication (IPC) calls. All devices launching with Android 8.0 or later must support binderized HALs only.
Last update: 2022-07-14
Table of Content
This guide is written for AOSP android-10.0.0_r47
From Android 12, you can not create any new HAL using HIDL! Refer to AIDL for HALs.
Binderized HAL#
In a Binderized HAL, the Android framework and HALs communicate with each other using binder inter-process communication (IPC) calls. All devices launching with Android O 8.0 or later must support binderized HALs only.
Framework Stacks#
Differences between Conventional HAL and Binderized HIDL for HAL:
Implementation#
Refer to Kernel Module to build and install a module to system. This guide assumes that invcase module is loaded as below:
+ on boot
+ insmod /system/lib/modules/invcase.ko
+ chown system system /dev/invcase
+ chmod 0600 /dev/invcase
Overview#
-
AOSP
-
build
- make
- target
-
product
-
base_vendor.mk
Include new packages+ PRODUCT_PACKAGES += \ + android.hardware.invcase@1.0-service \ + invcase_hidl_test \ + Invcase -
gsi
-
29.txt
Add new vendor native libraryVNDK-core: android.hardware.input.common@1.0.so + VNDK-core: android.hardware.invcase@1.0.so VNDK-core: android.hardware.ir@1.0.so
-
-
-
- target
- make
-
packages
- apps
-
Invcase
-
src
- com
- invcase
-
Invcase.java
Get InvcaseManager from SystemServiceclass Invcase extends Activity { InvcaseManager mManager; onCreate() { mManager = getSystemService(Context.INVCASE_SERVICE); } }
-
- invcase
- com
-
res
- layout
- mipmap
- values
-
AndroidManifest.xml
Export main activity on Launcher<manifest package="com.invcase" > <application> <activity android:name=".Invcase" android:exported="true" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>android:exported="true"is mandatory on Android 12 -
Android.bp
android_app { name: "Invcase", srcs: ["src/**/*.java"], platform_apis: true }platform_apis: true: use System API when do not specify any target platform
-
-
- apps
-
device
- generic
- car
- common
-
manifest.xml
Declare new interface+ <hal format="hidl"> + <name>android.hardware.invcase</name> + <transport>hwbinder</transport> + <version>1.0</version> + <interface> + <name>IInvcase</name> + <instance>default</instance> + </interface> + </hal>
-
- common
- car
- generic
-
frameworks
-
base
-
Android.bp
java_defaults { name: "framework-defaults", installable: true, srcs: [ + "core/java/android/hardware/invcase/IInvcaseManager.aidl", ] } -
api
-
current.txt
+ package android.hardware.invcase { + + public final class InvcaseManager { + method @NonNull public String getData(); + method public void putData(@NonNull String); + } + + }
-
-
core
- java
-
android
-
app
-
SystemServiceRegistry.java
Create an InvcaseManager instance and add it to the System Service list+ import android.hardware.invcase.InvcaseManager; public final class SystemServiceRegistry { static { + registerService(Context.INVCASE_SERVICE, InvcaseManager.class, + new CachedServiceFetcher<InvcaseManager>() { + @Override + public InvcaseManager createService(ContextImpl ctx) + throws ServiceNotFoundException { + return new InvcaseManager(ctx); + }}); } }
-
-
content
-
Context.java
Add Invcase Serive namepublic abstract class Context { + public static final String INVCASE_SERVICE = "invcase"; @StringDef(suffix = { "_SERVICE" }, value = { + INVCASE_SERVICE, }) }
-
-
hardware
-
invcase
-
IInvcaseManager.aidl
Define API for Invcase Interfaceinterface IInvcaseManager { getData(); putData(); } -
InvcaseManager.java
Use Invase Serive through the Invcase Interfaceclass InvcaseManager { IInvcaseManager mService; InvcaseManager(Context) throws ServiceNotFoundException { this(context, IInvcaseManager.Stub.asInterface( ServiceManager.getServiceOrThrow(Context.INVCASE_SERVICE)) ); } InvcaseManager(Context, IInvcaseManager){} getData() { mService.getData(); } putData() { mService.putData(); } }
-
-
-
-
- java
-
services
-
core
-
java
- com
- android
- server
- invcase
-
InvcaseService.java
Implement Invcase Interface functions, public the interfaceclass InvcaseService extends SystemService { IInvcaseManagerImpl extends IInvcaseManager.Stub { getData() { invcase_native_read(); } putData() { invcase_native_write(); } } mManagerService; onStart() { publishBinderService(Context.INVCASE_SERVICE, mManagerService); } }
-
- invcase
- server
- android
- com
-
jni
-
com_android_server_invcase_InvcaseService.cpp
Map java functions to native functions#include <hardware_legacy/invcase.h> jni_read () { invcase_read(); } jni_write () { invcase_write(); } static const JNINativeMethod method_table[] = { { "invcase_native_read", "()Ljava/lang/String;", (void*)jni_read }, { "invcase_native_write", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", (void*)jni_write }, }; register_android_server_InvcaseService(method_table); -
onload.cpp
Register mapped function callsnamespace android { + int register_android_server_InvcaseService(JNIEnv *env); }; extern "C" jint JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM* vm, void* /* reserved */) { + register_android_server_InvcaseService(env); } -
Android.bp
cc_library_static { srcs: [ + "com_android_server_invcase_InvcaseService.cpp", ], } cc_defaults { shared_libs: [ + "android.hardware.invcase@1.0", ], }
-
-
-
-
java
- com
- android
- server
-
SystemServer.java
Start Invcase Service+ import com.android.server.invcase.InvcaseService; public final class SystemServer implements Dumpable { private void startBootstrapServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) { + traceBeginAndSlog("StartInvcaseService"); + mSystemServiceManager.startService(InvcaseService.class); + traceEnd(); } }
-
- server
- android
- com
-
-
-
hardware
- interfaces
- invcase
-
1.0
-
default
- Android.bp
- Invcase.h
- Invcase.cpp
-
IInvcase.hal
interface IInvcase { putChars(string msg); getChars() generates (string msg); }; -
Android.bp
-
-
- invcase
- interfaces
-
Define HAL Interface#
Create a new HAL file in the folder hardware/interfaces:
package android.hardware.invcase@1.0;
interface IInvcase {
putChars(string msg);
getChars() generates (string msg);
};
Prepare HAL files#
Source
hidl-gen is a compiler for the HIDL (HAL Interface Design Language) which generates C++ and Java endpoints for RPC mechanisms. The main userspace libraries which this compiler uses can be found at system/libhidl.
Build hidl-gen if it is not built:
m hidl-gen
Then run it to generate C++ source file and Makefile:
export INVCASE_PACKAGE=android.hardware.invcase@1.0
export INVCASE_LOC=hardware/interfaces/invcase/1.0/default/
export HIDL_INF=android.hardware:hardware/interfaces
export HIDL_LIB=android.hidl:system/libhidl/transport
hidl-gen -o $INVCASE_LOC -Lc++-impl \
-r$HIDL_INF -r$HIDL_LIB $INVCASE_PACKAGE
hidl-gen -o $INVCASE_LOC -Landroidbp-impl \
-r$HIDL_INF -r$HIDL_LIB $INVCASE_PACKAGE
After these command, 3 files are generated in the default folder: Android.bp, Invcase.h, and Invcase.cpp. The generated files are for implement the HAL.
Service
Add three empty files for HAL service process in the 1.0/default folder:
android.hardware.invcase@1.0-service.rcandroid.hardware.invcase@1.0-service.xmlservice.cpp
Makefile
Run the tool:
./hardware/interfaces/update-makefiles.sh
to generate
// This file is autogenerated by hidl-gen -Landroidbp.
hidl_interface {
name: "android.hardware.invcase@1.0",
root: "android.hardware",
vndk: {
enabled: true,
},
srcs: [
"IInvcase.hal",
],
interfaces: [
"android.hidl.base@1.0",
],
gen_java: false,
}
Implement HAL#
Header:
#pragma once
#include <android/hardware/invcase/1.0/IInvcase.h>
#include <hidl/MQDescriptor.h>
#include <hidl/Status.h>
namespace android {
namespace hardware {
namespace invcase {
namespace V1_0 {
namespace implementation {
using ::android::hardware::hidl_array;
using ::android::hardware::hidl_memory;
using ::android::hardware::hidl_string;
using ::android::hardware::hidl_vec;
using ::android::hardware::Return;
using ::android::hardware::Void;
using ::android::sp;
struct Invcase : public IInvcase {
// Methods from ::android::hardware::invcase::V1_0::IInvcase follow.
Return<void> putChars(const hidl_string& msg) override;
Return<void> getChars(getChars_cb _hidl_cb) override;
// Methods from ::android::hidl::base::V1_0::IBase follow.
};
// FIXME: most likely delete, this is only for passthrough implementations
// extern "C" IInvcase* HIDL_FETCH_IInvcase(const char* name);
} // namespace implementation
} // namespace V1_0
} // namespace invcase
} // namespace hardware
} // namespace android
Source:
#define LOG_TAG "Invcase"
#include <utils/Log.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "Invcase.h"
namespace android {
namespace hardware {
namespace invcase {
namespace V1_0 {
namespace implementation {
// Methods from ::android::hardware::invcase::V1_0::IInvcase follow.
Return<void> Invcase::putChars(const hidl_string& msg) {
std::ofstream invcase_dev;
invcase_dev.open ("/dev/invcase");
if(invcase_dev.good()) {
invcase_dev << msg;
ALOGE("putChars: %s", msg.c_str());
} else {
ALOGE("putChars: can not open /dev/invcase");
}
return Void();
}
Return<void> Invcase::getChars(getChars_cb _hidl_cb) {
std::ifstream invcase_dev;
invcase_dev.open("/dev/invcase");
if(invcase_dev.good()) {
std::string line;
invcase_dev >> line;
ALOGE("getChars: %s", line.c_str());
hidl_string result(line);
_hidl_cb(result);
} else {
ALOGE("getChars: can not open /dev/invcase");
}
return Void();
}
// Methods from ::android::hidl::base::V1_0::IBase follow.
//IInvcase* HIDL_FETCH_IInvcase(const char* /* name */) {
//return new Invcase();
//}
//
} // namespace implementation
} // namespace V1_0
} // namespace invcase
} // namespace hardware
} // namespace android
Implement HAL Service#
To host the library we need to create a simple executable:
#define LOG_TAG "Invcase"
#include <iostream>
#include <android/hardware/invcase/1.0/IInvcase.h>
#include <hidl/HidlTransportSupport.h>
#include <hidl/LegacySupport.h>
#include <utils/Log.h>
#include "Invcase.h"
using android::hardware::invcase::V1_0::IInvcase;
using android::hardware::invcase::V1_0::implementation::Invcase;
using android::hardware::configureRpcThreadpool;
using android::hardware::joinRpcThreadpool;
using android::sp;
void logd(std::string msg) {
std::cout << msg << std::endl;
ALOGD("%s", msg.c_str());
}
void loge(std::string msg) {
std::cout << msg << std::endl;
ALOGE("%s", msg.c_str());
}
int main(int /* argc */, char** /* argv */) {
configureRpcThreadpool(1, true /*callerWillJoin*/);
android::sp<IInvcase> invcase = new Invcase();
if (invcase != nullptr) {
if (invcase->registerAsService() != ::android::OK) {
loge("Failed to register IInvcase service");
return -1;
}
} else {
loge("Failed to get IInvcase instance");
return -1;
}
logd("IInvcase service starts to join service pool");
joinRpcThreadpool();
return 1; // joinRpcThreadpool shouldn't exit
}
And request to start service at startup:
service vendor.invcase-1-0 /vendor/bin/hw/android.hardware.invcase@1.0-service
class hal
user system
group system
Makefile:
By default, hidl-gen creates a Makefile to build a shared library using the name android.hardware.invcase@1.0-service (note the suffix -service).
cc_binary {
name: "android.hardware.invcase@1.0-service",
defaults: ["hidl_defaults"],
vendor: true,
relative_install_path: "hw",
srcs: [
"service.cpp",
"Invcase.cpp"
],
init_rc: ["android.hardware.invcase@1.0-service.rc"],
shared_libs: [
"android.hardware.invcase@1.0",
"libhidlbase",
"libhidltransport",
"liblog",
"libutils",
],
vintf_fragments: ["android.hardware.invcase@1.0.xml"],
}
A test application that request the HAL service:
#define LOG_TAG "Invcase"
#include <iostream>
#include <android/hardware/invcase/1.0/IInvcase.h>
#include <hidl/HidlTransportSupport.h>
#include <hidl/LegacySupport.h>
#include <utils/Log.h>
#include <android/hardware/invcase/1.0/default/Invcase.h>
using android::hardware::invcase::V1_0::IInvcase;
using android::hardware::hidl_string;
using android::sp;
void logd(std::string msg) {
std::cout << msg << std::endl;
ALOGD("%s", msg.c_str());
}
void loge(std::string msg) {
std::cout << msg << std::endl;
ALOGE("%s", msg.c_str());
}
int main(int /* argc */, char** /* argv */) {
android::sp<IInvcase> invcase = IInvcase::getService();
if (invcase == nullptr) {
loge("Failed to get Invcase service");
return -1;
}
logd("Got Invcase service");
std::string msg = "Hello World!";
logd("Send: " + msg);
invcase->putChars(msg);
invcase->getChars([&](hidl_string result) {
logd("Receive: " + std::string(result));
});
return 0;
}
Build the test app:
cc_binary {
name: "invcase_hidl_test",
defaults: ["hidl_defaults"],
proprietary: true,
relative_install_path: "hw",
srcs: [
"invcase_hidl_test.cpp"
],
shared_libs: [
"android.hardware.invcase@1.0",
"libhidlbase",
"libhidltransport",
"libutils",
"liblog",
],
}
Define SELinux Policy for HAL service#
To make the service run at boot, HAL service needs to be registered to system under a security policy.
Declare the new type:
system/sepolicy/public/hwservice.te
type hal_invcase_hwservice, hwservice_manager_type;
Set compatibility
Ignore in API 28, which also ignore in API 27 and API 26:
system/sepolicy/private/compat/28.0/28.0.ignore.cil
(type new_objects)
(typeattribute new_objects)
(typeattributeset new_objects
( new_objects
hal_invcase_hwservice
)
)
Do not allow other apps to access:
system/sepolicy/private/app_neverallows.te
neverallow all_untrusted_apps {
hal_invcase_hwservice
}
Set service context interface:
system/sepolicy/private/hwservice_contexts
android.hardware.invcase::IInvcase u:object_r:hal_invcase_hwservice:s0
Declare attribute:
system/sepolicy/public/attributes
hal_attribute(invcase);
attribute hal_invcase;
attribute hal_invcase_client;
attribute hal_invcase_server;
Define default domain:
type hal_invcase_default, domain;
hal_server_domain(hal_invcase_default, hal_invcase)
type hal_invcase_default_exec, exec_type, vendor_file_type, vendor_file_type, file_type;
init_daemon_domain(hal_invcase_default)
Set binder policy:
system/sepolicy/public/hal_invcase.te
binder_call(hal_invcase_client, hal_invcase_server)
binder_call(hal_invcase_server, hal_invcase_client)
hal_attribute_hwservice(hal_invcase, hal_invcase_hwservice)
Set system context:
Note the HAL process path!
/(vendor|system/vendor)/bin/hw/android\.hardware\.invcase@1\.0-service u:object_r:hal_invcase_default_exec:s0
Declare system_server as client of HAL service:
system/sepolicy/private/system_server.te
hal_client_domain(system_server, hal_invcase)
Deliver HAL module#
VNDK
Vendor Native Development Kit (VNDK) is a set of libraries exclusively for vendors to implement their HALs. The VNDK ships in system.img and is dynamically linked to vendor code at runtime.
Refer to https://source.android.com/devices/architecture/vndk/build-system.
Include HAL service and the test app to the PRODUCT_PACKAGES:
+ PRODUCT_PACKAGES += \
+ android.hardware.invcase@1.0-service \
+ invcase_hidl_test \
This will include below files to system:
/vendor/lib/hw/android.hardware.invcase@1.0-service
/vendor/bin/hw/invcase_hidl_test
Export HAL Interface
Using show_make_tree.py to find the included manifest:
python show_make_tree.py \
"device/generic/car/aosp_car_x86_64.mk" \
"manifest.xml:"
File : device/generic/car/aosp_car_x86_64.mk
Inherit: device/generic/car/common/car.mk
Found : device/generic/car/common/manifest.xml:$(TARGET_COPY_OUT_VENDOR)/manifest.xml
Inherit: device/generic/goldfish/vendor.mk
Found : device/generic/goldfish/manifest.xml:$(TARGET_COPY_OUT_VENDOR)/manifest.xml \
Because car.mk inherits goldfish/vendor.mk, so file manifest.xml is copied from device/generic/car/common/manifest.xml as it is registered first. Read more about PRODUCT_COPY_FILES rules.
We add the HAL interface as below:
+ <hal format="hidl">
+ <name>android.hardware.invcase</name>
+ <transport>hwbinder</transport>
+ <version>1.0</version>
+ <interface>
+ <name>IInvcase</name>
+ <instance>default</instance>
+ </interface>
+ </hal>
API locked
If you encounter below error, it is because only Google can add interface into hardware/interfaces.
error: VNDK library list has been changed.
Changing the VNDK library list is not allowed in API locked branches.
You have to explicitly add the VNDK core to the API list:
VNDK-core: android.hardware.input.common@1.0.so
+ VNDK-core: android.hardware.invcase@1.0.so
VNDK-core: android.hardware.ir@1.0.so
JNI Wrapper#
The Java Native Interface (JNI) is a foreign function interface programming framework that enables Java code running in a Java virtual machine (JVM) to call and be called by native applications (programs specific to a hardware and operating system platform) and libraries written in other languages such as C, C++ and assembly.
-
Create java functions that call to native function in HAL library
jni_readcalls toinvcase_readjni_writecalls toinvcase_write
-
Register mapped functions with their signatures (encoded parameters)
-
Note that Java functions always have 2 default arguments:
JNIEnv* env: a structure containing methods that we can use our native code to access Java elementsjobject selfClass: the class of calling object
Implement JNI Mapping
Note that the function jniRegisterNativeMethods will register JNI functions for the class frameworks/services/core/java/com/android/server/invcase/InvcaseService.java:
#define LOG_TAG "Invcase"
#include "jni.h"
#include <nativehelper/JNIHelp.h>
#include "android_runtime/AndroidRuntime.h"
#include <utils/misc.h>
#include <utils/Log.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <android/hardware/invcase/1.0/IInvcase.h>
using android::hardware::invcase::V1_0::IInvcase;
using android::hardware::hidl_string;
namespace android
{
static void jni_init (
JNIEnv* /* env */,
jobject /* clazz */
) {
}
static void jni_deinit (
JNIEnv* /* env */,
jobject /* clazz */
) {
}
static jstring jni_read (
JNIEnv* env,
jobject /* clazz */
) {
sp<IInvcase> invcase = IInvcase::getService();
if (invcase == nullptr) {
ALOGE("JNI: Failed to get Invcase service\n");
return env->NewStringUTF("");
}
std::string msg;
invcase->getChars([&](hidl_string result) {
msg = std::string(result);
});
const char* buff = msg.c_str();
ALOGD("JNI: Receive: %s\n", buff);
return env->NewStringUTF(buff);
}
static void jni_write (
JNIEnv* env,
jobject /* clazz */,
jstring string
) {
sp<IInvcase> invcase = IInvcase::getService();
if (invcase == nullptr) {
ALOGE("JNI: Failed to get Invcase service\n");
return;
}
const char *buff = env->GetStringUTFChars(string, NULL);
ALOGD("JNI: Send: %s\n", buff);
invcase->putChars(std::string(buff));
}
static const JNINativeMethod method_table[] = {
{ "invcase_native_init", "()V", (void*)jni_init },
{ "invcase_native_deinit", "()V", (void*)jni_deinit },
{ "invcase_native_read", "()Ljava/lang/String;", (void*)jni_read },
{ "invcase_native_write", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", (void*)jni_write },
};
int register_android_server_InvcaseService(JNIEnv *env) {
ALOGD("JNI: register_android_server_InvcaseService\n");
return jniRegisterNativeMethods(
env,
"com/android/server/invcase/InvcaseService",
method_table,
NELEM(method_table)
);
}
}
Call the register function:
namespace android {
+ int register_android_server_InvcaseService(JNIEnv *env);
};
extern "C" jint JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM* vm, void* /* reserved */)
{
+ register_android_server_InvcaseService(env);
}
Build new JNI wrapper:
cc_library_static {
name: "libservices.core",
srcs: [
+ "com_android_server_invcase_InvcaseService.cpp",
],
}
cc_defaults {
name: "libservices.core-libs",
shared_libs: [
+ "android.hardware.invcase@1.0",
],
Declare API:
+ package android.hardware.invcase {
+ public final class InvcaseManager {
+ method @NonNull public String getData();
+ method public void putData(@NonNull String);
+ }
+ }
Service and Manager#
Define a name for new Service
public abstract class Context {
@StringDef(suffix = { "_SERVICE" }, value = {
+ INVCASE_SERVICE,
})
+ /**
+ * Use with {@link #getSystemService(String)} to retrieve a
+ * {@link android.hardware.invcase.InvcaseManager}.
+ *
+ * @see #getSystemService(String)
+ * @hide
+ */
+ public static final String INVCASE_SERVICE = "invcase";
Define the Service Interface
Use AIDL to describe public functions exported by the Service:
package android.hardware.invcase;
/**
* Invcase Manager interface
*
* {@hide}
*/
interface IInvcaseManager {
String getData();
void putData(String data);
}
Build AIDL:
java_defaults {
name: "framework-defaults",
installable: true,
srcs: [
+ "core/java/android/hardware/invcase/IInvcaseManager.aidl",
]
}
Implement the Service Manager
A Service Manager is the wrapper for the interface of the target Service which is obtained by calling to <Interface>.Stub.asInterface.
User application will call to the functions of the Service Manager, not directly calling to the actual service interface.
package android.hardware.invcase;
import android.annotation.NonNull;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.Log;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.os.ServiceManager;
import android.os.ServiceManager.ServiceNotFoundException;
public final class InvcaseManager {
static final String TAG = "Invcase";
private final Context mContext;
private final IInvcaseManager mService;
/**
* Creates a InvcaseManager.
*
* @hide
*/
public InvcaseManager(@NonNull Context context) throws ServiceNotFoundException {
this(context, IInvcaseManager.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getServiceOrThrow(Context.INVCASE_SERVICE)));
}
/**
* Creates a InvcaseManager with a provided service implementation.
*
* @hide
*/
public InvcaseManager(@NonNull Context context, @NonNull IInvcaseManager service) {
mContext = context;
mService = service;
Log.d(TAG, "InvcaseManager: mContext= " + mContext + " mService= " + mService);
}
public @NonNull String getData() {
try {
String str = mService.getData();
Log.d(TAG, "InvcaseManager: mService.getData= " + str);
return str;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public void putData(@NonNull String data) {
try {
Log.d(TAG, "InvcaseManager: mService.putData= " + data);
mService.putData(data);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Implement the Service
The Service will implement the actual code for Service Interface functions by extending the <Interface>.Stub class.
Note that JNI Native functions are exported to this object, therefore, it can call to HAL library’s functions.
package com.android.server.invcase;
import android.hardware.invcase.IInvcaseManager;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.Log;
import com.android.server.SystemService;
public class InvcaseService extends SystemService {
static final String TAG = "Invcase";
static final boolean DEBUG = false;
final IInvcaseManagerImpl mManagerService;
private final class IInvcaseManagerImpl extends IInvcaseManager.Stub {
@Override
public String getData() {
String str = invcase_native_read();
Log.d(TAG, "InvcaseService: IInvcaseManager.getData= " + str);
return str;
}
@Override
public void putData(String data) {
Log.d(TAG, "InvcaseService: IInvcaseManager.putData= " + data);
invcase_native_write(data);
}
}
public InvcaseService(Context context) {
super(context);
invcase_native_init();
mManagerService = new IInvcaseManagerImpl();
Log.d(TAG, "InvcaseService: mManagerService= " + mManagerService);
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
publishBinderService(Context.INVCASE_SERVICE, mManagerService);
Log.d(TAG, "InvcaseService: onStart");
}
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
invcase_native_deinit();
super.finalize();
}
private static native void invcase_native_init();
private static native void invcase_native_deinit();
private static native String invcase_native_read();
private static native void invcase_native_write(String string);
}
Run our service:
All system services are run in the same process called system_server which is implemented in the SystemServer.java. This process runs under system user.
import com.android.server.invcase.InvcaseService;
import android.util.Log;
public final class SystemServer implements Dumpable {
private void startBootstrapServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
+ // Manages Invcase device.
+ traceBeginAndSlog("StartInvcaseService");
+ Log.d("Invcase", "SystemServer: start InvcaseService");
+ mSystemServiceManager.startService(InvcaseService.class);
+ traceEnd();
User App#
The User App will be very simple to test the hardware. It contains an EditText to get user input, a Button to execute commands, and a TextView to display the result.
Implement the User App
- Use
getSystemService(Context.INVCASE_SERVICE)to obtain the instance ofInvcaseManager - Call to hardware through the
InvcaseManagerAPIs
package com.invcase;
import android.hardware.invcase.InvcaseManager;
import android.content.Context;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.util.Log;
public class Invcase extends Activity {
private static final String TAG = "Invcase";
private InvcaseManager mManager;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mManager = (InvcaseManager)getSystemService(Context.INVCASE_SERVICE);
Log.d(TAG, "App: mManager= " + mManager);
Button btn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
EditText editText = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText);
String txt = editText.getText().toString();
Log.d(TAG, "App: request= " + txt);
mManager.putData(txt);
String ret = mManager.getData();
Log.d(TAG, "App: received= " + ret);
TextView tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView);
tv.setText(ret);
}
});
}
}
Add User App to the Launcher
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.invcase" >
<application
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<activity
android:name=".Invcase"
android:exported="true"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
on Android 12, must use
android:exported="true"
Build User App
android_app {
name: "Invcase",
platform_apis: true,
srcs: [
"src/**/*.java"
]
}
Add User App to system packages:
+ PRODUCT_PACKAGES += \
+ Invcase
Permission#
The device /dev/invcase is created at boot with root permission.
The HAL Library is loaded when JNI Wrapper for Invcase Service is run, therefore, HAL code will run with system permission which attaches to the system_server process.
The Android Init Language uses init*.rc files to automatically do some actions when a condition is met.
For the target hardware, Android Init will use init.<hardware>.rc file. On Emulator, it is init.ranchu.rc.
Add below lines to change the owner and permission on the /dev/invcase at boot:
+ on boot
+ chown system system /dev/invcase
+ chmod 0600 /dev/invcase
Build and Run#
The Invcase Manager exports new Service APIs, therefore, need to rebuild the list of system APIs.
m all -j$(nproc)
Run the Emulator and run Invcase app:
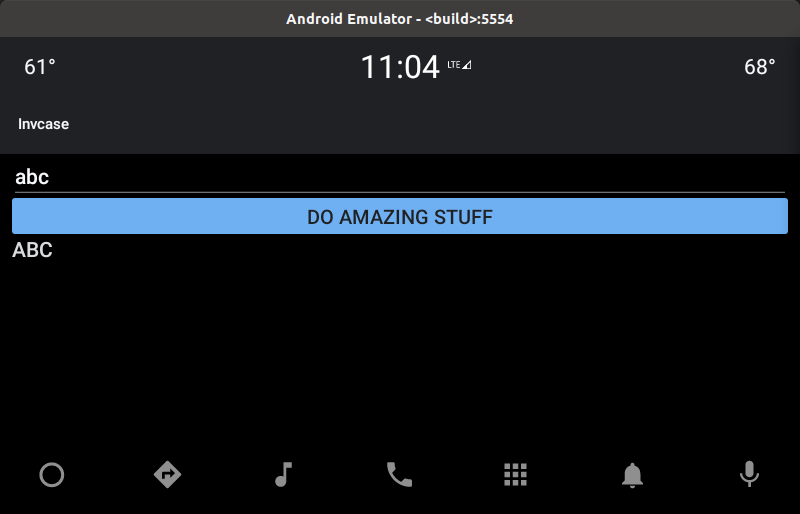
Start the Logcat to see debug lines:
logcat -s Invcase
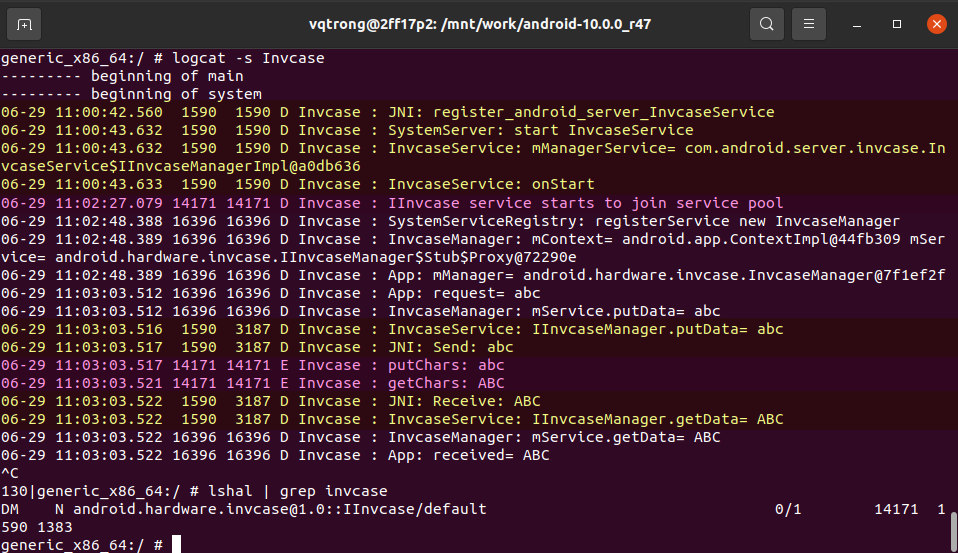
There are 3 processes:
-
The
system_serverprocess (yellow) does below things:- Load JNI functions
- Start Invcase Service whichs creates an object of Invcase Manager Implementation
-
The HAL process (purple) runs:
- Host the HAL implementation
-
The user app (white) process does below things:
- Load System Service Registry to have an object of Invcase Manager Interface
- Use received service interface to communicate with Invcase Manager Implementation in the Invcase Service